Public Key Infrastructure
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a widely accepted IT security framework based on 'Public Key Cryptography'. The Hong Kong Government has laid a solid foundation for deployment of PKI through the enactment of the Electronic Transactions Ordinance and the establishment of a public Certification Authority (CA) through the Hongkong Post.
Public Key Infrastructure Technology
PKI provides a management framework for enabling deployment of public key cryptography. Public key cryptography processes data with a pair of keys, which are two distinct but corresponding computer codes. Encryption is done with one of the key-pair and decryption is only possible with the use of the other key in the same pair.
One of the keys in the pair is kept by the owner of the certificate (as a personal secret), and is therefore called a 'private key'. The other key is publicly available, and hence called a 'public key'.
Encryption is the means by which the PKI ensures confidentiality. For instance, the privacy of messages sent via email can be protected by encryption with a recipient's public key. Since only the recipient's private key can decrypt the encrypted message, this is an assurance that nobody other than the intended recipient can read the message.
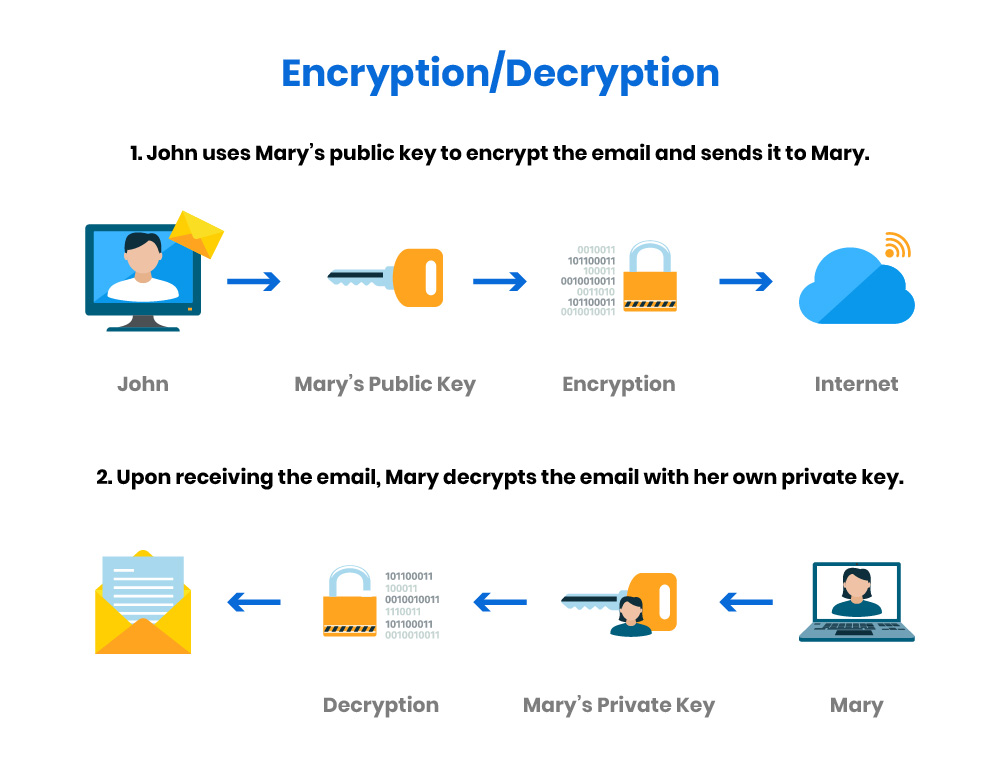
A digital signature is another means to ensure integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation. A digital signature is derived by applying a mathematical function to compute the message digest of an electronic message or document, and then encrypt the result of the computation with the signer's private key. Recipients can verify the digital signature with the use of the sender's public key.
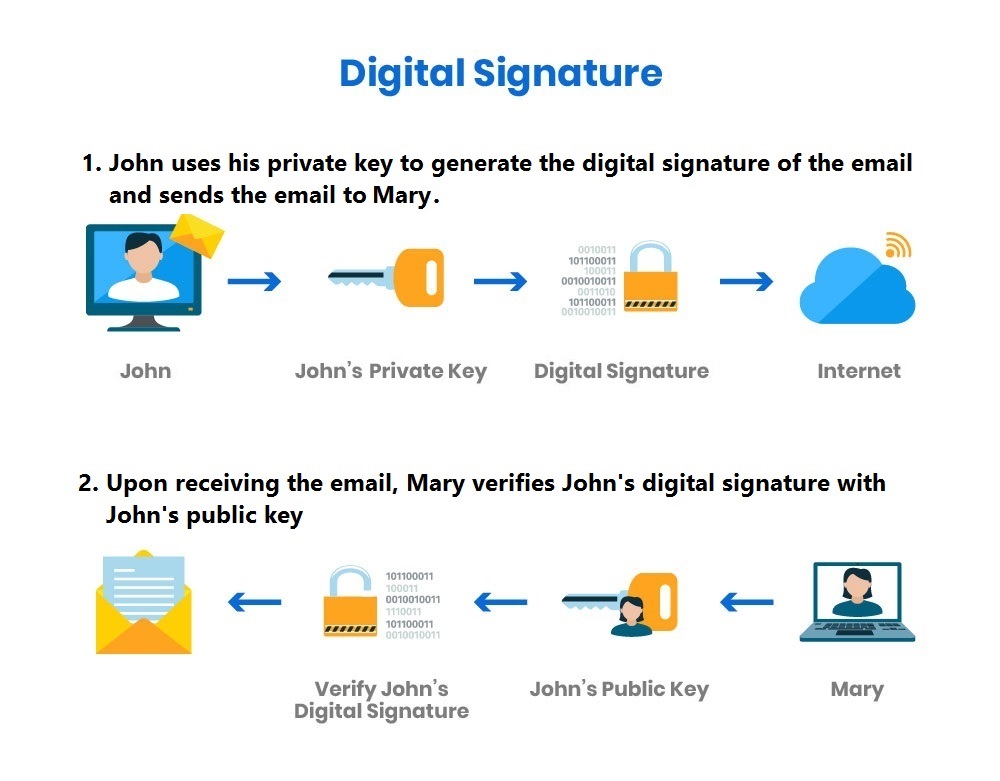
Taking email as an example, if a digitally signed email has not been tampered with during the course of transmission (integrity), the digital signature will be valid as verified by the recipient. Since the sender is the only person who has access to the corresponding private key, once the digital signature is verified as valid, the recipient can be certain that the email is indeed from the sender (ensuring authenticity); and the sender cannot deny having created and signed the email (non-repudiation).
Certification Authorities and Digital Certificates
The effective operation of PKI very much depends on the support of a CA. The main role of a CA is to act as a trusted third party to verify the identity of digital certificate subscribers.
The Hongkong Post is the first publically recognised CA under the Electronic Transactions Ordinance ("ETO") (Cap. 553). Any organisation and member of the public can buy digital certificates in Hong Kong from Hongkong Post, and they issue different types of digital certificate such as e-Certs, Bank-Certs and Mobile e-Certs. There are also a number of other recognised CAs under the Electronic Transactions Ordinance.
